How to capitalise on the world’s largest free trade pact
After nearly a decade in the making, the world's largest free trade pact finally kicked in on the first day of 2022.
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is the latest Free Trade Agreement (FTA) that aims to boost free trade among some of the most exciting growth regions in the world. Among others, RCEP will look to slash tariffs and red tape while enhancing connectivity and flow of goods and services across borders.
With the 15 members making up almost a third of the world’s population (2.2 billion) and global gross domestic product (US$29.7 trillion), RCEP will open enormous market opportunities for companies in the region.
In the next 20 years, RCEP signatories plan to eliminate duties imposed by each member state on 92 per cent of goods traded.
Where RCEP stands
By the end of January 2022, 12 of the 15 countries – Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand and Vietnam – have ratified the trade agreement. RCEP is currently in force in all these countries except Malaysia, which will commence on March 18, 2022.
For the three remaining ASEAN countries that have signed the agreement, Indonesia is likely to ratify RCEP in the first quarter of 2022[1]; the Philippines is waiting on its senate to ratify the country’s membership[2]; and Myanmar’s ratification is still awaiting acceptance by other members[3].
Once ratified, RCEP will come into force 60 days after countries deposit their instrument of ratification with the Secretary-General of ASEAN.
New markets, lower barriers
Traders can enjoy preferential market access and tariff treatment under RCEP, as long as goods comply with the rules of origin as set out in the trade pact. For starters, exporters will need to ensure that products marked for export have at least 20 per cent of the total value of materials that are obtained locally or sourced from ASEAN.
Manufacturers will also have more opportunities to qualify for preferential duties as they are now able to cumulate originating materials or components from more countries as compared to existing FTAs. This will mean greater supply chain flexibility for businesses.
Beyond tariff reduction, RCEP aims to be a fair and open multilateral trading system where customs, investment, intellectual property and e-commerce regulations are standardised. With simplified procedures to determine the rules of origin and other customs procedures, this significantly improves market access by lowering barriers to trade and streamlining customs clearance processes.
RCEP also opens doors to new markets. For the first time ever, three of Asia’s four largest economies – China, Japan and South Korea – will be connected by an FTA.
A one-stop trade advisory platform
As RCEP joins hundreds of FTAs around the world, finding the best applicable FTA with the most benefits can mean significant savings. But determining the harmonised system (HS) code of products and applying the best available FTA tax deductions is a common pain point for many trading, logistics and manufacturing businesses when calculating the shipment’s Total Landed Cost (TLC).
With a global supply chain platform such as CALISTA Intelligent Advisory (CIA), users can easily find HS codes, keep up with the latest trade advisory requirements and calculate the shipment’s TLC.
To start off, users enter a product description – even in layman’s terms – and the system can recommend the most relevant HS code and its associated product description, thanks to its advanced natural language processing engine.
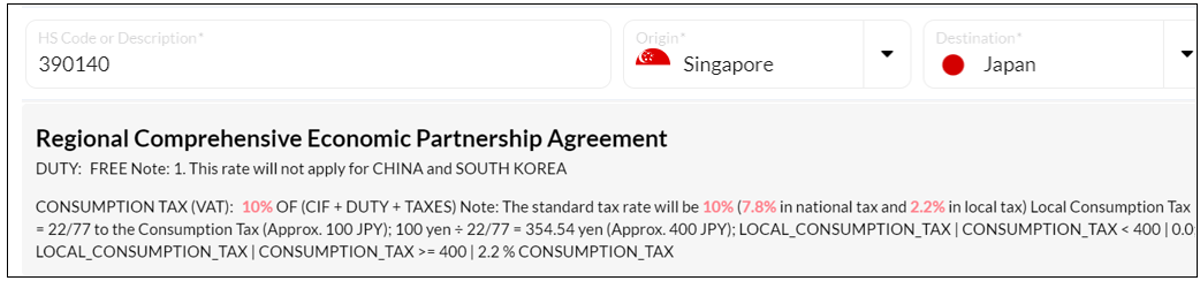
A breakdown of applicable RCEP FTA Duties on bio-polyethene products exported from Singapore to Japan.This can be found under the ‘Duties and Taxes’ Tab in CIA’s compliance eAdvisory.
After selecting a country pair listed under an FTA like RCEP, you can view the associated RCEP FTA duties applicable to the HS code.
Comparison of tariff concessions and TLCs between most-favoured-nation clause (MFN) and RCEP on apples exported from Japan to Vietnam.
Users can also compare the TLC based on various applicable FTAs and select the best available ones that qualify for the most amount of tax deductions. In the above example, RCEP significantly reduces the TLC on apples exported from Japan to Vietnam compared with the most-favoured-nation (MFN) clause.
Are you a trading, logistics or manufacturing business looking for a one-stop solution to maximise your profits through RCEP? Check out CALISTA intelligent advisory (CIA).